Pre-connection Attack
Pre-connection attack is the first part of the network penetration testing. To perform this attack, we will look at the fundamentals like how to show all the networks around us, how to find the details of all the connected devices to a particular network. Once we know about the network and connected devices to it, we can disconnect any device without knowing the password of that device.
Following are the basic steps we will be going through to perform Pre-connection attack:
- Wireless Interface in Monitor mode: In this step, we will change the mode of wireless device as Monitor mode.
- About airodump-ng: In this step, we will use airodump-ng to list all the network around us and display useful information about them.
- Run airodump-ng: In this step, we will see all the devices that are connected to a particular network and collect more information about it.
- Deauthenticate the Wireless client: In this step, we can disconnect any device which is shown in the previous step using the aireplay-ng.
Wireless interface in Monitor Mode
This step is used to put your wireless card into Monitor mode. In Monitor mode, your card can listen to every packets that's around us. By default, the mode of wireless devices is set to "Managed" that means our wireless device will only capture packets that have our device's MAC address as the destination MAC. It will only capture packets that are actually directly to my Kali machine.
But we want to capture all the packets that are within our range even if the destination MAC is not our MAC or even without knowing the password of the target device. To do this, we need to set the mode as Monitor mode.
We can use iwconfig to see the wireless interfaces.
Where
- ifconfig wlan0 down command is used for disabling the Managed mode
- airmon-ng check kill command is used to kill any process that could interfere with using my interface in monitor mode. After this command, your internet connection will be lost.
- iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor command is used to enable monitor mode
- ifconfig wlan0 up command is used to enable the interface
- iwconfig command shows that the mode is set to Monitor
In the above figure, you can see that the mode is changed as Monitor mode. Now we are able to capture all the Wi-Fi packets that are within our range even if the packets are not directed to our computer or even without knowing the password of the target network.
To do this, we need a program that can capture the packets for us. The program we are going to use is airodump-ng.
About airodump-ng
airdump-ng is used to list all the network around us and display useful information about them. It is a packet sniffer, so it is basically designed to capture all the packets around us while we are in Monitor mode. We can run it against all of the networks around us and collect useful information like the mac address, channel name, encryption type, number of clients connected to the network and then start targeting to the target network. We can also run it against certain AP(access point) so that we only capture packets from a certain Wi-Fi network.
Syntax
- airodump-ng [MonitorModeInterface]
First, let's look at how to run the program. In this case, we need our Wi-Fi card in Monitor mode. The name of the our Wi-Fi card is wlan0.
Note: We can press Ctrl + C to stop the following execution.
- BSSID shows the MAC address of the target network
- PWR shows the signal strength of the network. Higher the number has better signal
- Beacons are the frames send by the network in order to broadcast its existence
- #Data, shows the number of data packets or the number of data frames
- #/s shows the number of data packets that we collect in the past 10 seconds
- CH shows the channel on which the network works on
- ENC shows the encryption used by the network. It can be WEP, OPN, WPA, WPA2
- CIPHER shows the cipher used in the network
- AUTH shows the authentication used on the network
- ESSID shows the name of the network
In the above image, you can show all the wireless networks like Oppo, perfe, Fligh, Ashu, LIFCA, Xiaom, BS1A-YW5 etc and the detailed information about all the network.
Run airodump-ng
In this step, we will run airodump-ng to see all the devices that are connected to a particular network and collect more information about it. Once we have a network to the target, it's useful to run airodump-ng on that network only, instead of running it on all the networks around us.
Currently, we are running airodump-ng on all the networks around us. Now we are going to target the network BS1A-YW5 whose BSSID is 50:C8:E5:AF:F6:33. We are going to sniff on that network only.
To do this, we will be use the same program. The command will be as follows:
Where
- --bssid 50:C8:E5:AF:F6:33 is the access point MAC address. It is used to eliminate extraneous traffic.
- --channel 11 is the channel for airodump-ng to snif on.
- --write test is used to store all the data in a file named as test. It is not mandatory, you can skip this part.
- wlan0 is the interface name in Monitor mode.
After execution of this command, the following devices will be shown:
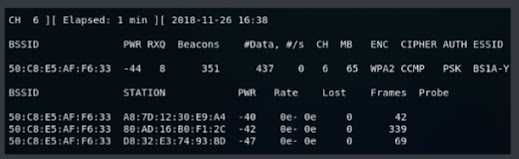
Where
- BSSID of all the devices is same because devices are connected to the same network
- STATION shows the number of devices that are connected to this network
- PWR shows the power strength of each of the devices
- Rate shows the speed
- Lost shows the amount of data loss
- Frames show the number of frames that we have captured
After executing this command, we have 3 devices that are connected to the network BS1A-YW5 and all the devices have the same BSSID as 50:C8:E5:AF:F6:33.
Deauthenticate the wireless client
It is also known as deauthentication attacks. These attacks are very useful. These attacks allow us to disconnect any device from any network that is within our range even if the network has encryption or uses a key.
In deauthentication attack, we are going to pretend to be client and send a deauthentication packet to the router by changing our MAC address to the MAC address of the client and tell the router that we want to disconnect from you. At the same time, we are going to pretend to be router by changing our MAC address to the router's MAC address until the client that we are requesting to be disconnected. After this, the connection will be lost. Through this process, we can disconnect or deauthenticate any client from any network. To do this, we will use a tool called aireplay-ng.
Syntax
After executing this command, the device whose STATION is A8:7D:12:30, lost the internet connection. We can only connect to the network again when we quit this executing command by pressing Ctrl + C.
Where- -deauth is used to tell airplay-ng that we want to run a deauthentication attack and assign 100000 which is the number of packets so that it keeps sending a deauthentication packets to both the router and client and keep the client disconnected.
- -a is used to specify the MAC address of the router. 50:C8:E5:AF:F6:33 is the target access point.
- -c specifies the MAC address of the client. A8:7D:12:30:E9:A4 is client's MAC address.
- wlan0 is the wireless adaptor in Monitor mode.





No comments:
Post a Comment